Mental Health and Athletes

Mental Health
Causes of Mental Stress in Athletes
Mental health is often a taboo topic, and even more so for athletes. The pressure to win, be the best, and push one's body to its limits can take a toll on mental health. Unfortunately, mental health issues in sport are all too common, but they are rarely talked about. This post will explore some of the most common mental health issues faced by athletes, as well as ways to manage them.Most Common Mental Health Concerns
The most common mental health issues faced by athletes are stress and anxiety. The pressure to perform can be overwhelming, and the fear of failure can be crippling. Stress and anxiety can lead to a number of other mental health issues, such as depression, insomnia, and feeling overwhelmed. It is important for athletes to find ways to manage their stress and anxiety in order to maintain their mental health.Why do Athletes have Mental Health Issues?
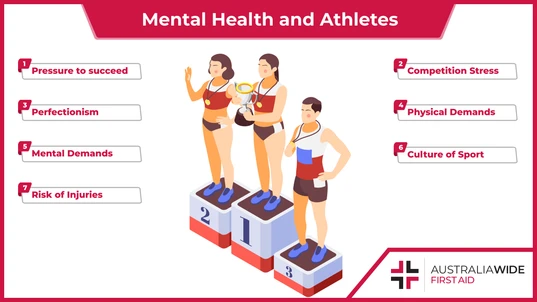
There are a number of factors that can contribute to mental health issues in athletes. The pressure to succeed can be overwhelming. Success in sport is often defined by winning, and athletes can feel a lot of pressure to win. This pressure can come from coaches, parents, fans, and even themselves. The fear of failure can be paralyzing, and the pressure to succeed can lead to mental health issues such as stress and anxiety. The competitive nature of sport can foster an environment of perfectionism, which can lead to unrealistic expectations and increased stress levels. Perfectionism is often a major contributor to mental health issues such as anxiety and depression. The physical demands of sport can be taxing on the body and mind, leading to fatigue and burnout. Burnout has symptoms such as mental and physical exhaustion, cynicism, and a decreased sense of accomplishment. Burnout is a major contributor to mental health issues such as depression and anxiety. The culture of sport can be a major contributor to mental health issues. The macho culture of many sports can discourage athletes from seeking help for mental health issues. The culture of sport often dictates that athletes should be tough and mentally strong, which can lead to mental health issues being ignored or denied. The mental demands of sport can be just as taxing as the physical demands. The constant focus on performance can lead to mental fatigue and burnout. The mental demands of sport can also lead to anxiety and depression. Injuries can cause mental health issues by preventing athletes from participating in their sport or achieving their goals. When injured, athletes can feel isolated, frustrated, disappointed and angry. These feelings can lead to mental health issues such as depression and anxiety. All of these factors are contributors to mental health issues in athletes. It is important for athletes to be aware of these factors and find ways to manage them in order to maintain their mental health.Managing Mental Health in Sport
There are a number of ways to manage stress and anxiety. Some coping mechanisms include: Regular exercise: Exercise is a great way to reduce stress and improve mental health. It releases endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects. Deep breathing: Deep breathing helps to calm the body and mind. It can be done anywhere, at any time. Yoga: Yoga is a great way to stretch the body and calm the mind. It can be done at home or in a studio. Meditation: Meditation helps to focus the mind and clear away racing thoughts. It can be done anywhere, at any time. Talking to someone: Talking to someone about what is stressing you out can help to put things into perspective and make them seem more manageable. This could be a friend, family member, therapist, or coach. Eating healthy: Eating a nutritious diet helps to improve mental health. It is important to eat balanced meals and snacks that are high in nutrients. Getting enough sleep: Sleep is crucial for mental health. Most people need 7-8 hours of sleep per night. Limiting alcohol intake: Alcohol is a depressant and can worsen mental health symptoms. It is important to drink in moderation or not at all. Take a break: Sometimes, the best thing to do is to take a break from training or competition. This will help to prevent burnout and allow the body and mind to recover. Have positive self-talk: Negative self-talk can worsen mental health symptoms. It is important to talk to yourself in a positive way. Find an activity that makes you happy: Doing things that make you happy can help to improve mental health. This could be listening to music, spending time with friends and family, or doing a hobby. If you are an athlete struggling with mental health issues, please seek help from a mental health professional. They will be able to assess your situation and provide you with the necessary tools to manage your mental health.Mental Health Support
Education really is the key to a society that honours mental health. Without proper education, misconceptions and stigmas can impact how mental health is viewed, and stop people from getting the help they need. Mental health is just as integral to your wellbeing as physical health. Knowing how to recognise the signs and symptoms of mental ill-health early can ensure that people get timely help. This intervention can prevent mental health crises, which can be life-threatening events. Completing a Mental Health Support Course gives you the knowledge and tools to recognise when someone is struggling or in a crisis, and how to help. If an in-person course doesn't suit you, we also offer a fully-online Mental Health Support course to give you the knowledge and tools you need to be able to assist someone who is experiencing poor mental health or is in a crisis. Completed from the comfort of your own home, earn your Certificate of Completion to give to your employer, put on your resume, or simply move forward with the knowledge that you can lend actual help to those who may need it.
Originally published at
https://www.australiawidefirstaid.com.au/resources/mental-health-and-athletes
as part of the Australia Wide First Aid Articles Library









